Liver diseases are on the rise, with non-alcoholic diseases becoming increasingly common among youth. Lifestyle factors such as diet play a crucial role in the development of liver disease. One of the most important dietary choices is the type of cooking oil you use daily. From the sautéed veggies to the seared fish you have for lunch, cooking oil has a crucial role in making the food healthy or unhealthy. So, what oil should you be opting for to keep your liver healthy? Let’s take a look.
Olive oil

Olive oil tops the list, thanks to its liver-protecting properties. It is a staple in the Mediterranean diet, which is considered the best eating pattern in the world, and also ideal for reversing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Studies have consistently shown that extra virgin olive oil protects the liver by decreasing inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. A 2015 review of nine trials found that olive oil may also help reduce liver enzymes and liver fat that contribute to disease. The monounsaturated fatty acids in olive oil promote better metabolic health.
Avocado oil
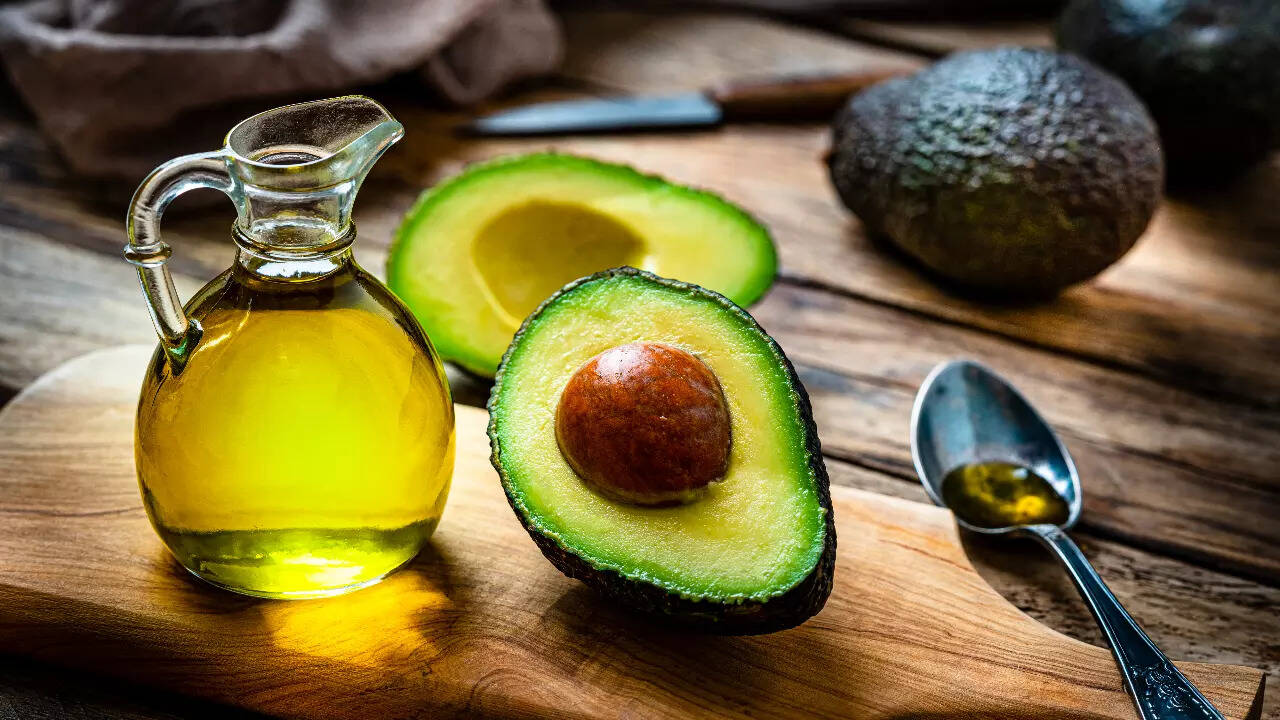

It has a high smoke point of around 520 degrees Fahrenheit and is good for deep frying states Dr Sethi.
Consider avocado oil as a sibling of olive oil. It stands next to olive oil, and is known for its high smoke point and rich nutrient profile. A 2022 study in rats found that avocado oil alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by improving mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Avocado oil also protects the liver, thanks to its monounsaturated fats and phenols. As it is stable and has a buttery flavour, it’s best for higher heat cooking such as stir-fries. Avocado oil is often known as the ‘olive oil of the Americans’, as it has a similar fat composition to olive oil.
Olive oil vs avocado oil
So, which oil is better? Olive oil or avocado oil? While both oils are ideal for cooking, considering the liver-protecting benefits, which one to use really depends on your individual needs and liking. For instance, olive oil is ideal for low to medium-heat cooking, as it has a lower smoke point. So it’s best to use for sautéing or stir-frying veggies, drizzling on dishes, and salad dressings. It is rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenol antioxidants that reduce inflammation and protect the liver.Avocado oil, on the other hand, is best for high-heat cooking, due to its high smoke point. So, it’s perfect for roasting, grilling, and frying. Rich in monounsaturated fats and vitamin E, this oil also protects the liver against oxidative stress and helps in liver detoxification. It is a safe option for searing or frying, where olive oil may burn.
Oils to avoid or limit

- Coconut oil
- Palm oil
- Ghee
- Butter
- Partially hydrogenated oils (trans fats)
- Sunflower oil
- Corn and soybean oils
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making changes to your diet, lifestyle, or treatment plan, especially if you have liver disease or other medical conditions.