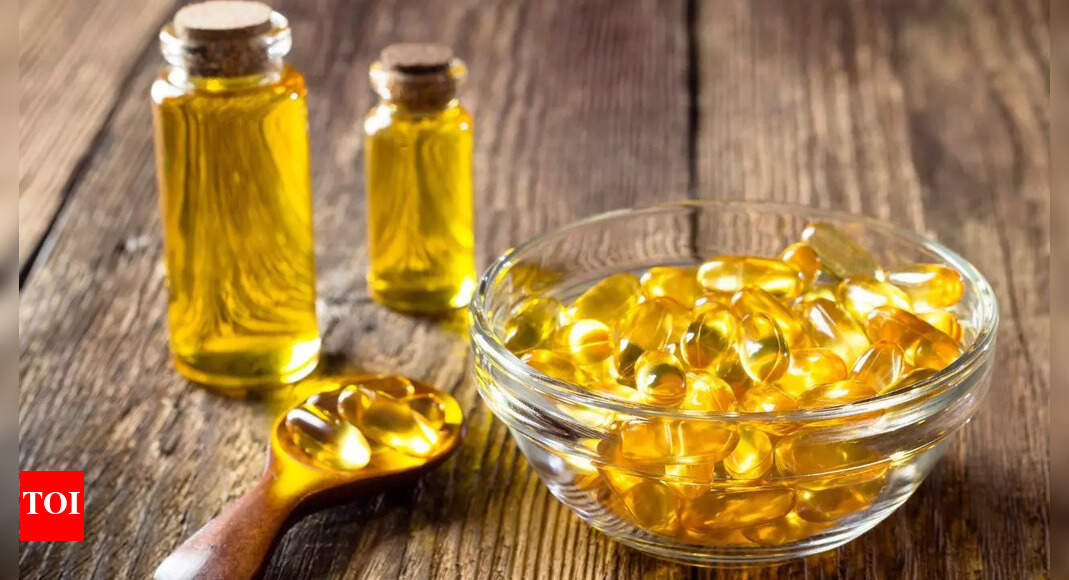
Fish oil supplements, extracted from fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are among the most widely used nutritional aids worldwide. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), they support cardiovascular health, brain function, vision, joint flexibility, and even skin wellness. But while many people know why fish oil is beneficial, fewer realise that when you take it can influence how well your body absorbs and uses these fatty acids. Since omega-3s are fat-soluble, timing, meal composition, and consistency all matter. Understanding the best time to take fish oil can help you unlock maximum health benefits.
How timing affects fish oil absorption
Unlike water-soluble vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids dissolve in fat. This means that your body cannot efficiently absorb fish oil on an empty stomach or with low-fat meals. Taking fish oil alongside food that contains dietary fat enhances the absorption process, allowing omega-3s to travel through the digestive system and be distributed where they’re needed most.
- Morning vs Night: Some people prefer taking supplements in the morning to avoid forgetting, while others notice better tolerance in the evening. Research suggests that both timings can be effective, provided the supplement is consumed with a fat-containing meal.
- Consistency over timing: What truly matters is building a routine. Consistent intake helps maintain steady omega-3 levels in the blood, ensuring long-term benefits for heart, brain, and joint health.
- Meal composition matters: A breakfast of toast and coffee won’t provide enough fat for good absorption, but pairing fish oil with eggs, avocado, or nut butter will.
Best time of day to take fish oil
The best time to take fish oil often depends on your lifestyle and meals. A study in the Frontiers of Nutrition highlights that taking omega-3s with dietary fat improves absorption, making morning, evening, or split doses effective as long as they’re paired with a balanced meal.1. Morning with breakfastTaking fish oil in the morning works well for those who eat a balanced breakfast containing healthy fats. Adding your capsule alongside eggs, yogurt with nuts, or avocado toast ensures maximum absorption. Morning intake can also provide an energy and focus boost throughout the day, thanks to DHA’s role in brain and nerve function. For busy people, this is also the easiest way to stay consistent, since forgetting nighttime doses is more common.2. Evening with dinnerIf your morning meals are light, taking fish oil with dinner may be more effective. Dinner typically contains more substantial fats, like olive oil, fish, or meat, which aid omega-3 absorption. Some studies also suggest that consuming omega-3s later in the day may help reduce nighttime inflammation, supporting overnight muscle recovery and potentially improving sleep quality. Evening doses may also reduce the chances of experiencing fishy burps during working hours.3. Split doses (Morning + night)For people taking higher doses, splitting fish oil into two smaller servings can enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. Dividing the dose also helps maintain more stable omega-3 levels throughout the day, which can be especially beneficial for individuals managing inflammation, arthritis, or cardiovascular concerns.
Health benefits of fish oil
Regular fish oil supplementation supports numerous aspects of health:
- Heart health: Omega-3s reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, and help prevent arterial plaque buildup. Studies suggest consistent intake lowers the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Brain function: DHA is a major structural fat in the brain and retina. Adequate levels support memory, focus, learning, and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline with age
- Joint and muscle support: EPA helps reduce inflammation, easing stiffness and pain in conditions like arthritis. Athletes also use omega-3s for faster post-exercise recovery.
- Eye health: DHA supports retinal function and can reduce the risk of dry eyes and macular degeneration.
- Skin and hair: Omega-3s nourish skin cells, reducing dryness, inflammation, and acne, while promoting healthy scalp circulation.
- Pregnancy and child development: Adequate omega-3 intake during pregnancy supports fetal brain and eye development and may reduce the risk of postpartum depression.
Common side effects of fish oil and how to minimise them
While fish oil is generally safe, some users experience digestive issues such as nausea, diarrhea, or “fishy burps.” These usually occur when supplements are taken incorrectly. To minimise discomfort:
- Always take fish oil with meals containing fat for smoother digestion.
- Try enteric-coated capsules or triglyceride-form fish oil, which reduce aftertaste and are absorbed better.
- Split higher doses into two smaller servings to avoid stomach upset.
- Store supplements in the refrigerator to reduce burping and maintain freshness.
- Opt for high-quality brands that use molecular distillation to remove contaminants and ensure purity.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health routine or treatment.