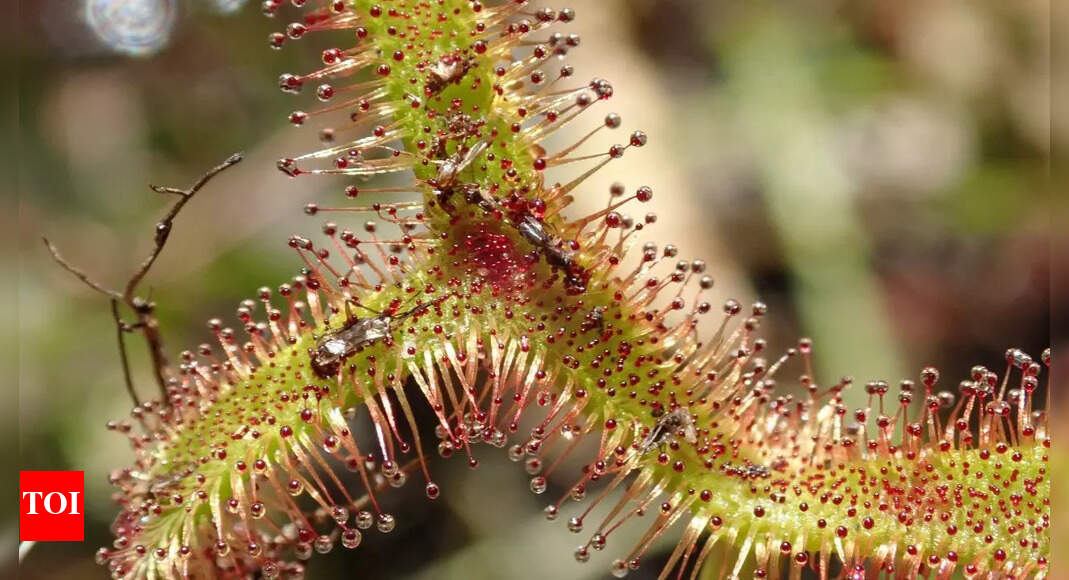
Carnivorous plants are unique species that have adapted to survive in nutrient-poor environments by capturing and digesting insects and other small organisms. Instead of relying solely on the soil for nutrients, they use specialized trapping mechanisms, such as sticky surfaces, snap traps, and pitfall cups, to obtain essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus. Popular types include Venus flytraps, sundews, pitcher plants, and bladderworts, each with its fascinating way of trapping prey. These adaptations allow them to thrive in habitats where most other plants cannot, making them both ecologically important and incredibly intriguing to botanists and nature enthusiasts alike.
What are carnivorous plants and their different types
Carnivorous plants, also known as insectivorous plants, are plants that obtain essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, by capturing and digesting insects, spiders, and other small animals. These plants have evolved specialized structures and mechanisms to attract, trap, and digest their prey, allowing them to thrive in environments where other plants would struggle to survive.1. Venus flytrap: Perhaps the most iconic carnivorous plant, the Venus flytrap has modified leaves that can snap shut quickly to capture insects.
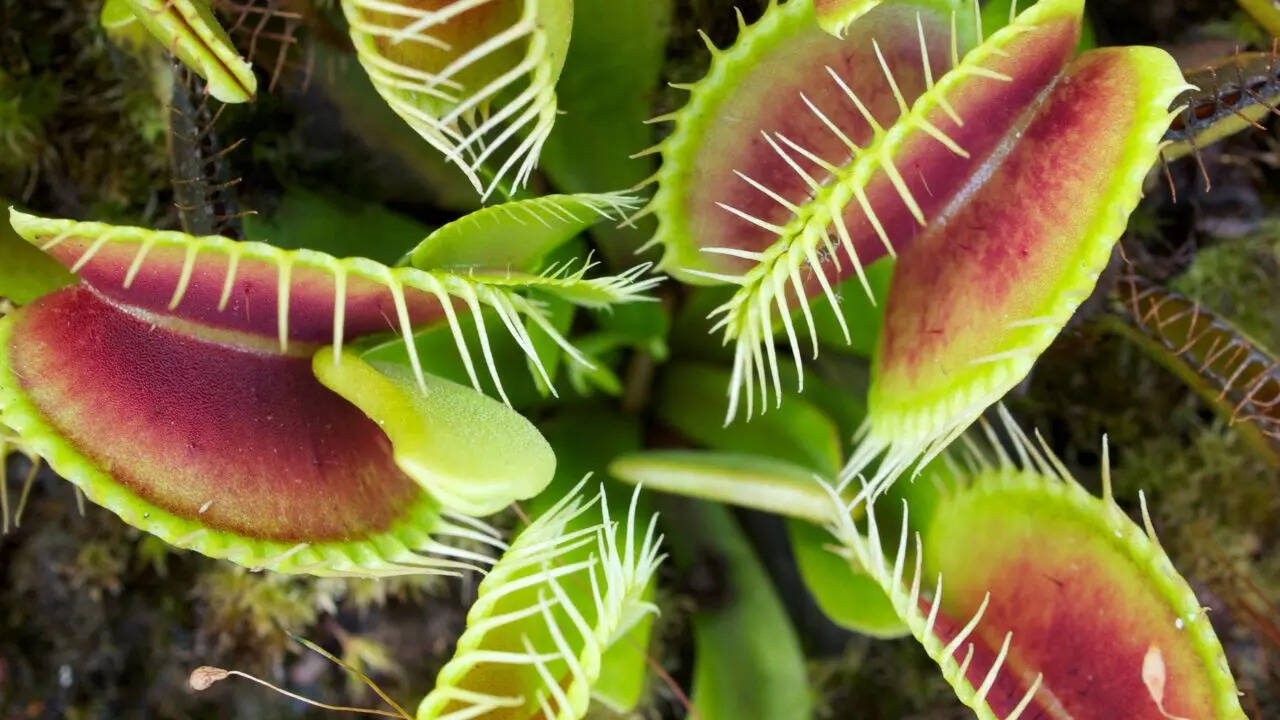

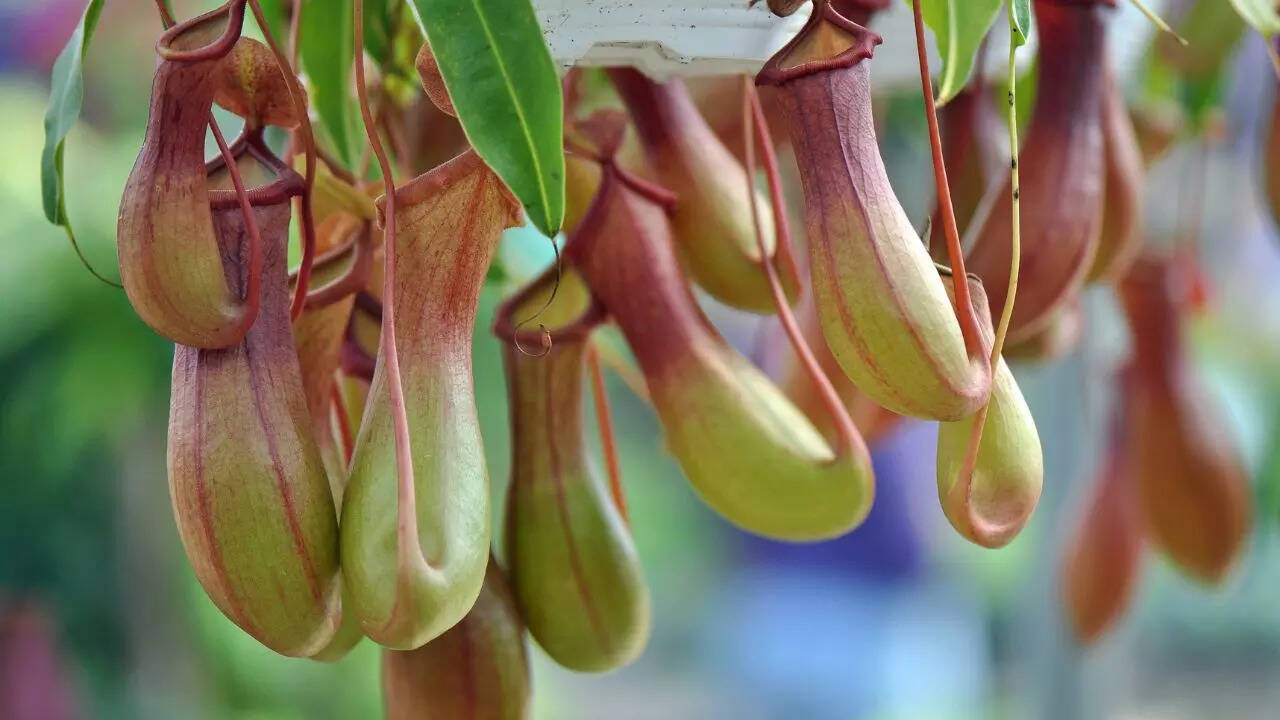
2. Pitcher plants: These plants have deep, slippery cups that attract insects, which they cannot escape from. Enzymes produced by the plant then digest the insects.

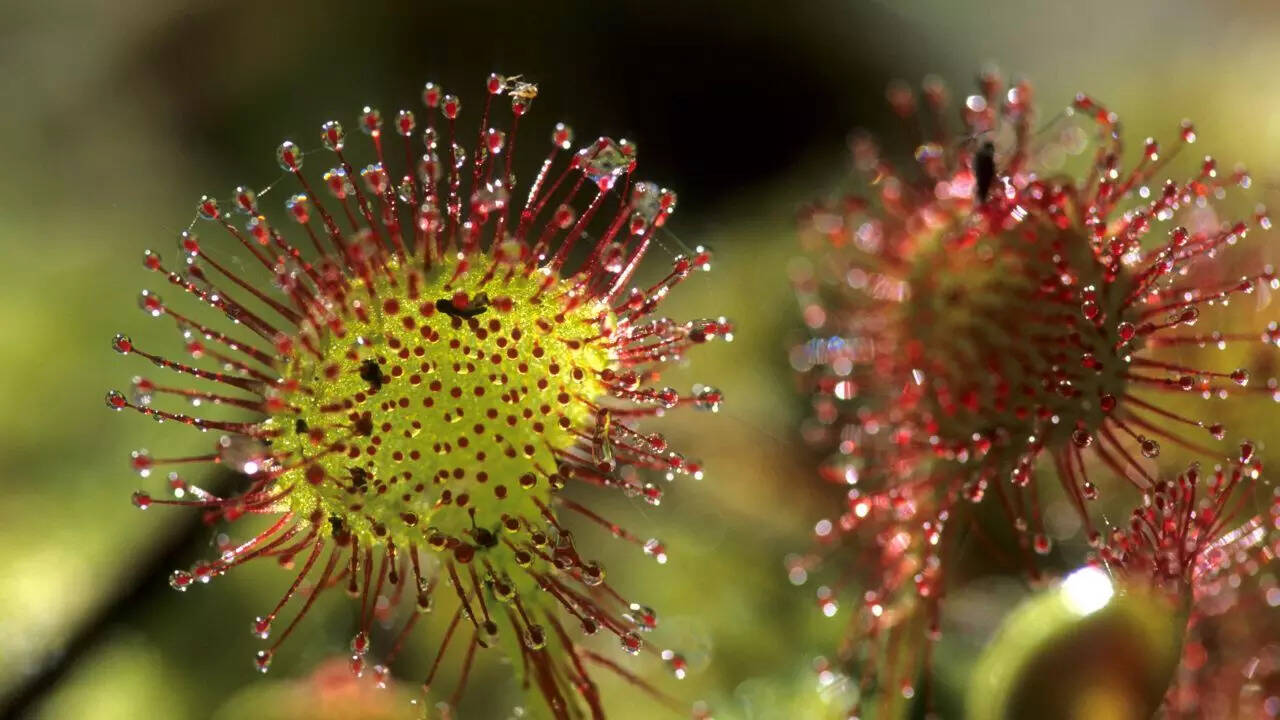
Sundews: Sundews have leaves covered in sticky droplets of a glue-like substance that trap insects. The leaves then curl around the prey to digest it.

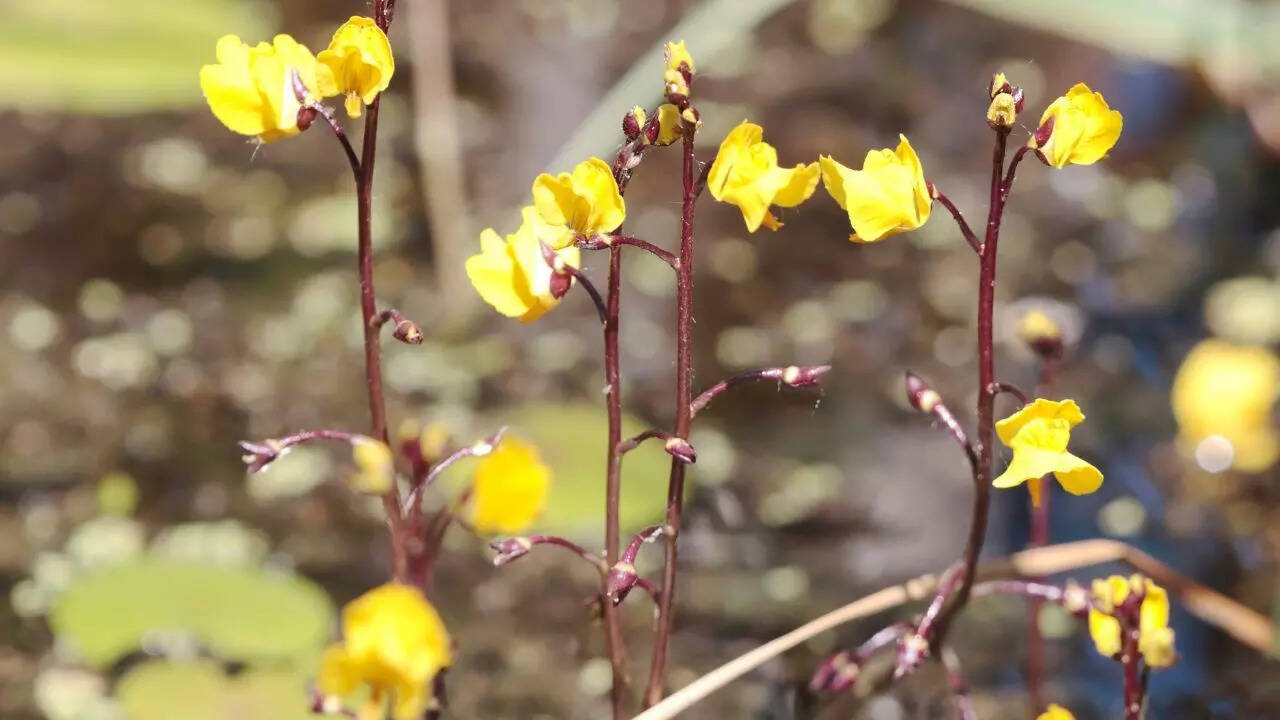
Bladderworts: These plants have bladder-like traps that capture small organisms, such as protozoa and insects, by sucking them in quickly.

How do carnivorous plants capture their prey
- Snap traps: Venus flytraps and other snap trap plants have modified leaves that can snap shut quickly to capture insects. This is triggered by the movement of insects across trigger hairs on the leaves.
- Sticky traps: Sundews and other sticky trap plants have leaves covered in sticky droplets of a glue-like substance that trap insects. The leaves then curl around the prey to digest it.
- Pitfall traps: Pitcher plants have deep, slippery cups that insects fall into and cannot escape from. Enzymes produced by the plant then digest the insects.
Why do carnivorous plants thrive in nutrient-poor environments
- Adaptation to low nutrient environments: Carnivorous plants have evolved to thrive in environments where other plants would struggle to survive due to a lack of essential nutrients.
- Supplemental nutrition: By capturing and digesting prey, carnivorous plants can obtain essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, that are lacking in their environment.