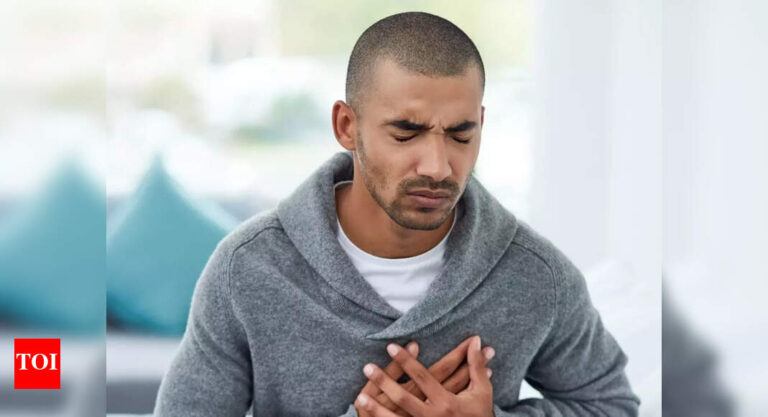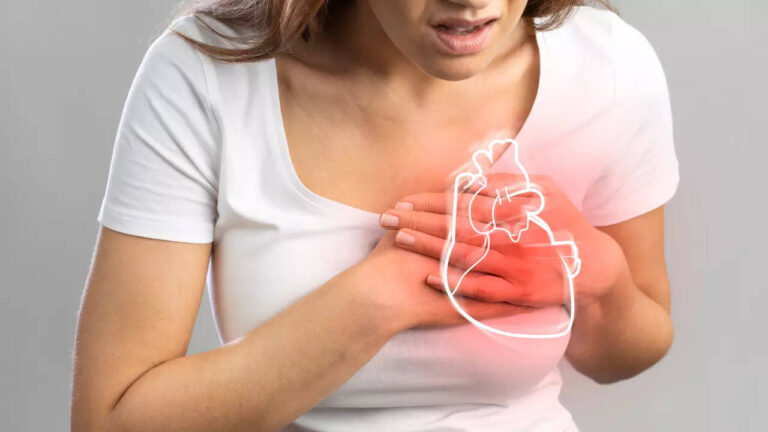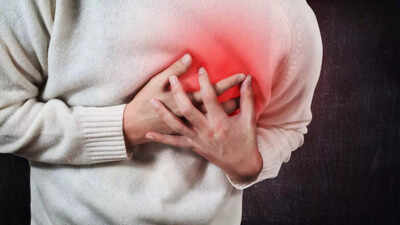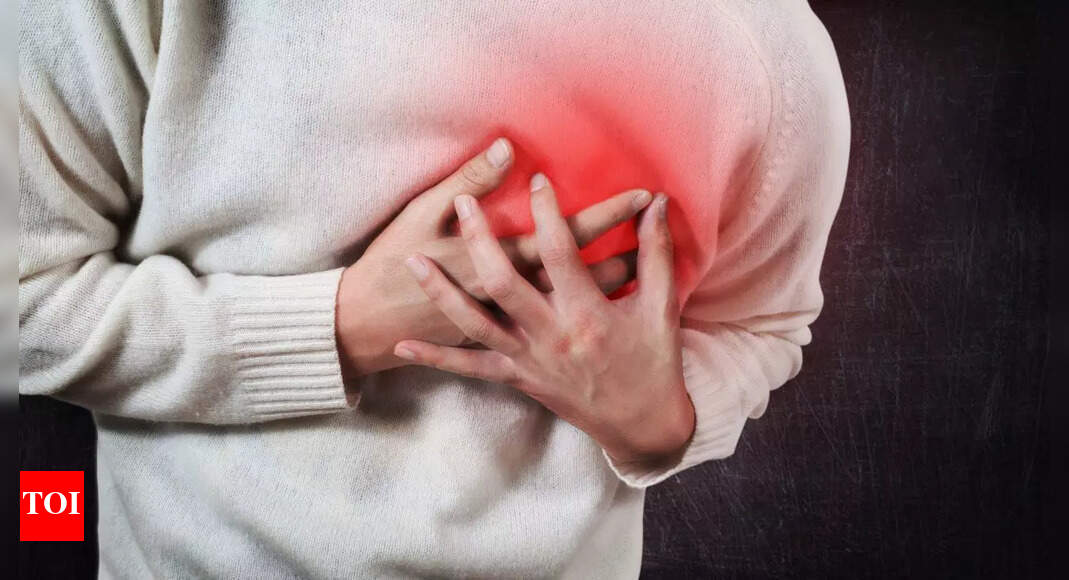
Experiencing chest pain and breathlessness can be frightening, often making people worry about a heart attack. However, medical experts emphasise that not all chest pain is heart-related. Even though cardiovascular disease is increasingly common worldwide, studies show that over half of chest pain cases in hospitals stem from non-cardiac causes. These can include stress, anxiety, lung issues, or gastrointestinal problems, all of which can mimic heart attack symptoms. Recognizing the underlying conditions, their warning signs, and risk factors is essential for accurate diagnosis. Timely medical evaluation helps distinguish between serious heart emergencies and reversible non-cardiac issues, ensuring appropriate treatment and reducing unnecessary anxiety for patients.
Understanding non-cardiac chest pain
Chest pain does not always originate from the heart. There are numerous non-cardiac conditions that can trigger similar symptoms, including musculoskeletal injuries, acid reflux, lung infections, anxiety, or even panic attacks. While these conditions are less life-threatening than a heart attack, medical evaluation is critical because the symptoms can overlap.Doctors emphasise that anyone experiencing sudden chest pain or breathlessness should seek immediate medical attention to rule out serious heart issues, even if it ultimately turns out to be non-cardiac.
What is ‘broken heart syndrome ’
One notable condition that can mimic a heart attack is Broken Heart Syndrome, also called stress-induced cardiomyopathy or Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. This temporary heart condition occurs when extreme physical or emotional stress rapidly weakens a portion of the heart muscle. As a result, the rest of the heart may work harder to compensate, producing symptoms similar to a heart attack.
How broken heart syndrome differs from a heart attack
Broken Heart Syndrome differs from a classic heart attack in several important ways:
- It is not caused by blocked coronary arteries.
- It usually does not cause permanent heart damage.
- Symptoms appear suddenly, often following intense stress.
Recovery is typically fast and complete, unlike heart attacks which may leave lasting cardiac impairment.
Causes of broken heart syndrome
While the precise cause of Broken Heart Syndrome is not fully understood, doctors believe that sudden emotional or physical stress plays a key role. Stressors such as a relationship breakup, the death of a loved one, a severe accident, job loss, or serious illness can trigger the condition.The body responds to stress by releasing stress hormones, which may temporarily interfere with normal heart function. In some cases, no obvious trigger is identified, highlighting the complex nature of this syndrome. Notably, there is no evidence of hereditary transmission; it cannot be passed from parents to children.
Broken heart syndrome signs and symptoms
Symptoms often appear within minutes to hours of a stressful event. Because the heart muscle is temporarily stunned, the condition can mimic the classic signs of a heart attack. Common symptoms include:
- Severe chest pain or angina
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Weakening of the left ventricle
- Irregular heartbeats or palpitations
- Low blood pressure
- Fainting or dizziness
- Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for receiving prompt medical care.
Broken heart syndrome: Who is more at risk
Certain individuals are more prone to developing Broken Heart Syndrome. Key risk factors include:
- Female gender, particularly women over 50
- Age above 50 years
- History of psychiatric conditions, such as anxiety or depression
- History of neurological disorders, such as seizures or stroke
- Awareness of these risk factors can help both patients and healthcare providers identify those at higher risk and monitor them closely during stressful situations.
When to seek medical helpEven though Broken Heart Syndrome is reversible and usually non-fatal, chest pain and breathlessness should never be ignored. Immediate medical attention is essential to rule out life-threatening conditions, ensure proper diagnosis, and initiate treatment.Also Read | Reverse migraine pain naturally: Hidden acupressure points and simple techniques to reduce headaches and boost energy