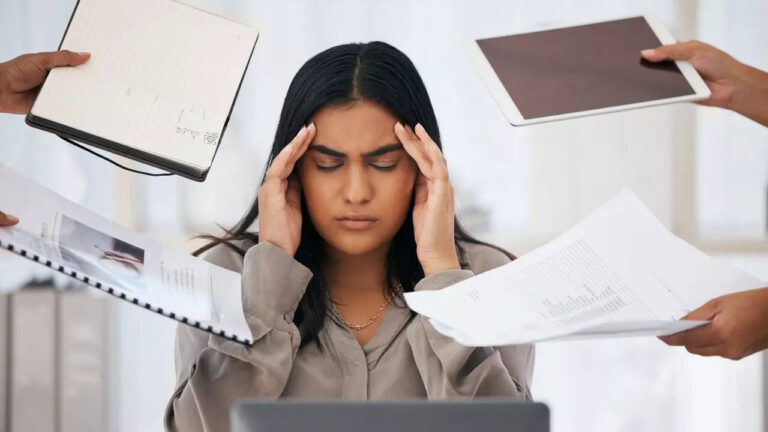
Calcium deficiency, or hypocalcemia, occurs when calcium levels in the body drop below normal, affecting key functions like muscle movement, nerve signaling, and bone strength. Often caused by medical conditions, medications, or poor absorption rather than diet alone, this deficiency can lead to symptoms such as muscle cramps, fatigue, brittle nails, dry skin, and even dental issues. In severe cases, it may cause seizures, irregular heartbeats, or osteoporosis. Recognising early signs like tingling in the fingers or frequent muscle pain is essential. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment, including supplements and dietary changes, can help prevent long-term complications of calcium deficiency.
Understanding calcium deficiency and its common signs and symptoms
Calcium deficiency, also known as hypocalcemia, occurs when the body has insufficient calcium to support vital functions like bone strength, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling. While it can result from low dietary intake, it’s more commonly caused by underlying health conditions or medications. Over time, untreated calcium deficiency can lead to serious complications affecting the bones, teeth, muscles, and even the heart.1. Muscle cramps and spasmsOne of the earliest signs of calcium deficiency is painful muscle cramps, spasms, or twitching, often in the legs, arms, or back.2. Numbness and tinglingA tingling or “pins and needles” sensation in the hands, feet, or around the mouth may indicate low calcium levels affecting nerve function.3. Fatigue and weaknessConstant tiredness, lack of energy, and overall muscle weakness can result from calcium-deficient cells not functioning efficiently.4. Dry skin and brittle nailsA lack of calcium can lead to dry, itchy skin and fragile nails that break or split easily.5. Hair loss and coarse hair textureHair may become dry, rough, and may fall out in patches due to the body’s inability to nourish follicles properly.6. Bone pain and fragilityChronic calcium deficiency weakens the bones, causing pain, fractures, osteopenia, and over time, osteoporosis.7. Dental issuesCalcium is essential for strong teeth—its deficiency can lead to brittle teeth, cavities, irritated gums, and tooth decay.8. Irregular heartbeat (Arrhythmia)Low calcium can affect heart muscle contraction, potentially leading to irregular heart rhythms or palpitations.9. Severe premenstrual symptoms (PMS)In women, calcium deficiency may contribute to more intense PMS symptoms such as mood swings, cramps, and bloating.10. Cognitive problemsBrain fog, memory issues, confusion, and difficulty concentrating may stem from inadequate calcium in brain cells.11. Depression and mood changesLow calcium levels may be linked to depression, anxiety, or irritability due to its effect on brain and nerve function.12. Seizures in severe casesIn extreme cases, severe calcium deficiency can trigger convulsions or seizures due to disrupted nerve signaling.13. Poor immune responseA calcium-deprived body may struggle to fight infections, leading to more frequent illness and slower recovery.14. Growth issues in childrenIn growing children, calcium deficiency can lead to delayed development, poor bone growth, and dental abnormalities.15. Dizziness or lightheadednessSome individuals may experience dizziness or balance issues due to low calcium affecting the nervous system.Also read | Chikungunya symptoms that might go unnoticed